A review of the salt freezing and denitrification process for chemical nitrate-containing wastewater
Published Time:
2021-12-16
Source:
Author:
Article Publication
Recently, China Well and Mine Salt successfully published
Honzon Company focuses on innovation of new technologies, research and development of new processes and products, and attaches importance to R&D investment. It has made continuous breakthroughs in research achievements and has now developed into a world-class provider of zero-discharge wastewater solutions and membrane equipment supplier.
The chemical nitrate wastewater desalination process is widely used in the environmental protection field. This article compares and analyzes the composition characteristics of chemical nitrate wastewater and the technical and economic aspects of the applied salt and cold crystallization technology, and draws preliminary conclusions on each process route.
Publication Details

Magazine Article Inside Pages
Original Text Summary
I. Existing Chemical Nitrate Wastewater Desalination and Cold Crystallization Technology
The components of nitrate wastewater from a certain coal chemical enterprise are shown in Table 1.
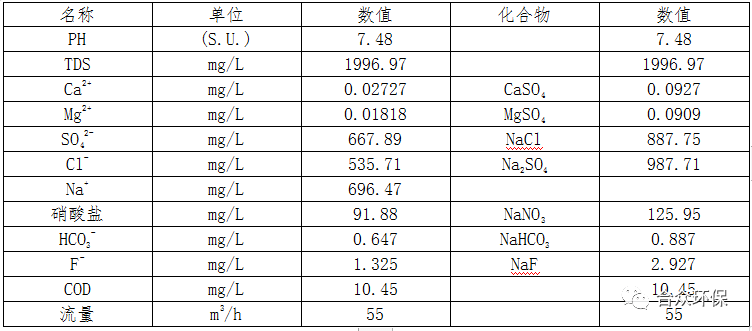
Table 1 Nitrate Wastewater Components
Analysis of Table 1 shows that the nitrate wastewater has complex components, including sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, sodium nitrate, magnesium sulfate, calcium sulfate, sodium fluoride, sodium bicarbonate, COD, etc.
After pretreatment, chemical wastewater usually contains salt, nitrate, and COD. Due to the presence of COD, traditional processes such as thermal salt-nitrate coproduction are limited, and the investment risk of the equipment is increased. Therefore, in recent years, the industry's environmental protection projects have used cold crystallization technology for nitrate separation, and the existing chemical nitrate wastewater desalination and cold crystallization technologies mainly include:
1.1 Evaporation denitrification, cold crystallization, and evaporation desalination process (referred to as Process 1)
The components of the reverse osmosis concentrated brine from a certain coal chemical enterprise after pretreatment are shown in Table 2.
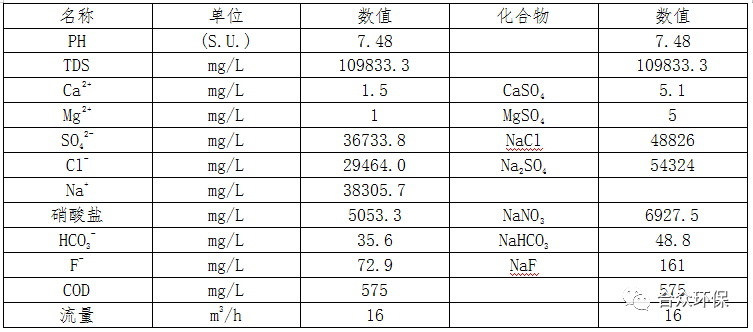
Table 2 Reverse Osmosis Concentrated Brine Components
Using reverse osmosis concentrated brine as raw material, the process flow of evaporation denitrification, cold crystallization, and evaporation desalination (Process 1) is shown in Figure 1.
Using reverse osmosis concentrated brine as raw material, sodium sulfate is obtained by evaporation and concentration crystallization. The nitrate mother liquor is frozen to obtain mirabilite, which is returned to the evaporation denitrification process to recover sodium sulfate. The cold crystallization refined brine is evaporated to obtain sodium chloride, and the salt-making mother liquor is dried to obtain mixed salt.
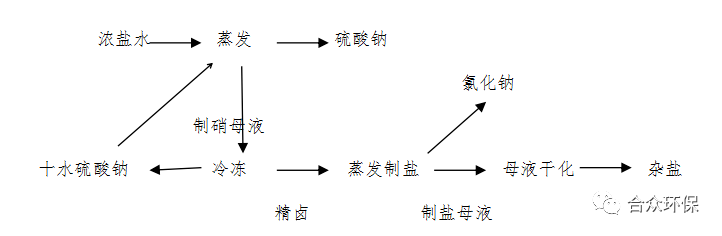
Figure 1 Process Flow Diagram of Evaporation Denitrification, Cold Crystallization, and Evaporation Desalination (Process 1)
1.2 Nanofiltration, cold crystallization, evaporation desalination, and evaporation denitrification process (referred to as Process 2)
The components of the nanofiltration dilute brine and concentrated brine after pretreatment of nitrate wastewater are shown in Table 3 and Table 4, respectively.
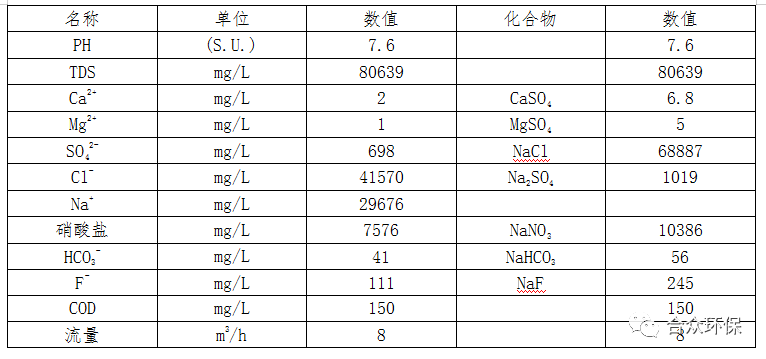
Table 3 Nanofiltration Dilute Brine Components
Analysis of Table 3 shows that sodium chloride is precipitated first by evaporating the nanofiltration dilute brine of nitrate wastewater, and then other components are concentrated and saturated.
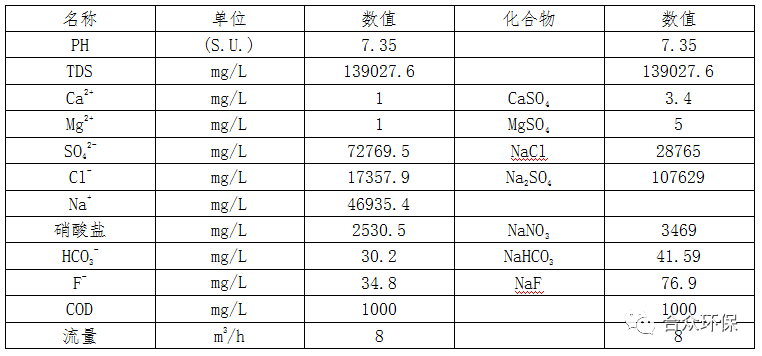
Table 4 Nanofiltration Concentrated Brine Components
Analysis of Table 4 shows that sodium sulfate is precipitated first by evaporating the nanofiltration concentrated brine of nitrate wastewater, and then other components are concentrated and saturated.
Based on the above Table 1-3 nanofiltration dilute brine and Table 1-4 nanofiltration concentrated brine components, the process flow of nanofiltration, cold crystallization, evaporation desalination, and evaporation denitrification (Process 2) is shown in Figure 2.
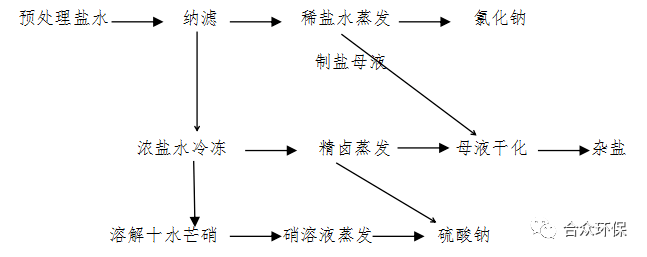
Figure 2 Process Flow Diagram of Nanofiltration, Cold Crystallization, Evaporation Desalination, and Evaporation Denitrification (Process 2)
Using pretreated brine as raw material, solutions mainly containing sodium chloride (dilute brine) and sodium sulfate (concentrated brine) are obtained through pretreatment and nanofiltration. Mirabilite is obtained by freezing the concentrated brine; sodium chloride is obtained by evaporating the dilute brine; sodium sulfate is obtained by evaporating the dissolved mirabilite solution and the precipitated nitrate mother liquor; and mixed salt is obtained by drying the salt-making mother liquor and the nitrate-making mother liquor.
II. Technical and Economic Analysis of the Processes
2.1 Technical and Economic Analysis of Process 1
Sodium sulfate and nitrate mother liquor are obtained by evaporation and crystallization of reverse osmosis concentrated brine. The amount of nitrate mother liquor is small, and the refrigeration load is small; the reasonable utilization of equipment for recovering sodium sulfate by returning mirabilite to the evaporation denitrification process is conducive to reducing investment; the sodium chloride evaporation process is rich in COD, with many impurities in the evaporation crystallization, and poor salt quality affecting its use; the end point of salt-making mother liquor evaporation is affected by the salt-nitrate coprecipitation point and COD concentration, the amount of salt-making mother liquor is small, and less mixed salt is obtained by drying.
2.2 Technical and Economic Analysis of Process 2
Using pretreated brine as raw material, solutions mainly containing sodium chloride (dilute brine) and sodium sulfate (concentrated brine) are obtained through pretreatment and nanofiltration; the sodium chloride (dilute brine) contains less COD and sodium sulfate, and the quality of the evaporated salt is better, which is beneficial to downstream use;
Mirabilite and refined brine are obtained by freezing the concentrated brine, with a large freezing amount and high energy consumption; sodium sulfate is obtained by evaporating the refined brine and the dissolved mirabilite solution separately, the equipment setting is unreasonable, and the investment is increased; the refined brine contains high calcium, magnesium, and COD concentrations, which affect the evaporation and cleaning cycle and the amount of discharged mother liquor; the amount of salt-making mother liquor and nitrate-making mother liquor at the evaporation end point is large, and more mixed salt is obtained by drying.
III. Process Improvement Suggestions
3.1 Improvement Suggestions for Process 1
Suggested process improvements: Add measures to remove calcium and magnesium from the bittern and reduce COD, improve sodium chloride evaporation conditions to obtain better salt quality, and expand the uses of salt.
3.2 Improved Suggestions for Process Two
Suggested process improvements: In the salt making process, add a brine freezing process to increase the recovery rate of sodium sulfate and reduce the amount of impurities; add measures to remove calcium and magnesium from the bittern and reduce COD, improve sodium sulfate evaporation conditions and reduce the amount of impurities; in the decahydrate mirabilite return to bittern evaporation process, reduce the investment in the sodium sulfate evaporation process.
Recommended Dynamics








